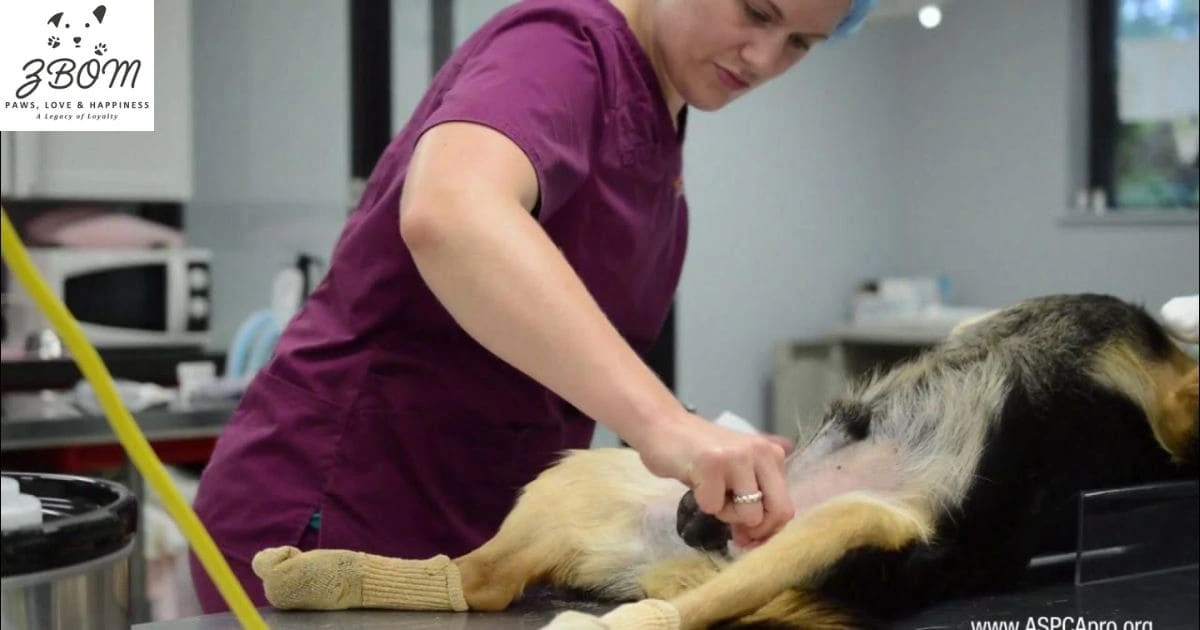
Getting Your Dog Neutered
Getting Your Dog Neutered, Neutering your dog is one of the most responsible decisions a pet owner can make, yet it often comes with questions, concerns, and even myths. Simply put, neutering is a surgical procedure that removes a male dog’s testicles, preventing him from reproducing. While some owners may hesitate because of misconceptions about pain, behavior changes, or health risks, the reality is that neutering is a safe, routine procedure with many long-term benefits for both your dog and your household.
Beyond preventing unwanted litters, neutering can have a significant positive impact on your dog’s health. It reduces the risk of certain cancers, such as testicular cancer, and can lower the likelihood of prostate problems later in life. Behaviorally, neutered dogs are often calmer, less aggressive, and less prone to roaming in search of a mate. This can lead to a safer environment for your dog and reduce the chances of accidents, fights, or stress for both you and your pet.
It’s also a socially responsible choice. With countless dogs in shelters awaiting homes, preventing unplanned litters helps reduce the number of homeless animals and eases the strain on rescue organizations. Many veterinarians emphasize that neutering is not just about population control; it’s about enhancing the quality of life for your dog while supporting community animal welfare.
Also Read: German Shepherd Vs Golden Retriever
Understanding the process, recovery, and long-term effects can help you make a well-informed decision. With proper care and guidance from your veterinarian, neutering can be a straightforward experience with minimal stress for your dog. This introduction explores the reasons, benefits, and considerations behind neutering, offering insights to help every dog owner make the choice that ensures a healthier, happier life for their furry companion.

Short Answer About: What Is Dog Neutering
Getting Your Dog Neutered, Dog neutering is a common surgical procedure in which a veterinarian removes a male dog’s testicles, making him unable to reproduce. It’s often referred to as “castration” and is considered a routine, safe operation when performed by a qualified professional. The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia, and most dogs recover quickly with proper post-operative care.
Also Read: When Do German Shepherds Go into Heat
Neutering is not just about preventing unwanted puppies; it also offers significant health and behavioral benefits. For example, neutered dogs have a lower risk of testicular cancer and certain prostate problems. Behaviorally, neutering can reduce aggression, lessen the urge to roam in search of a mate, and decrease marking or mounting behaviors. These changes often make dogs calmer and easier to manage at home.
It’s also a responsible step for pet owners concerned with community animal welfare. By preventing unplanned litters, neutering helps reduce the number of homeless dogs and supports shelters in managing pet populations.
Overall, dog neutering is a safe, effective, and humane choice that contributes to the long-term health and happiness of your pet. With proper veterinary care and post-surgery attention, most dogs recover fully and continue to live active, joyful lives.
What Is Dog Neutering
Dog neutering is one of the most common and responsible decisions a pet owner can make for their male dog. Often referred to as male dog castration, the neuter procedure involves the surgical removal of a dog’s testicles. This procedure ensures that the dog cannot reproduce, helping to prevent unwanted litters while also offering numerous health and behavioral benefits.
Also Read: What Vaccines do Dogs Need
The neuter procedure is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring that the dog remains completely pain-free during the surgery. Getting Your Dog Neutered, Veterinarians take great care to minimize discomfort and provide guidance for proper post-operative care. For most pet owners, understanding that this is a pain-free surgery helps ease concerns and supports a positive experience for their dog.
Neutering is considered the most common dog surgery, and the majority of pet dogs undergo this operation at some point in their lives. Despite its frequency, the ideal neutering age remains a topic of discussion among veterinarians. Getting Your Dog Neutered, Some research suggests early neutering may have health or behavioral implications, while other studies indicate benefits to waiting until the dog is older. This ongoing neutering controversy means that owners should discuss the best timing for their individual dog with a qualified veterinarian.
Also Read: How are Heartworms Transmitted in Dogs
Beyond preventing reproduction, dog neutering contributes significantly to dog reproductive health. It reduces the risk of testicular cancer and certain prostate issues, promoting a longer and healthier life. Additionally, neutering can positively influence behavior, often resulting in calmer dogs who are less prone to aggression, roaming, or marking territory. These behavioral improvements make daily life easier for owners and support responsible pet ownership.
As a routine dog operation, neutering is straightforward when performed by trained professionals. Many veterinary clinics offer guidance on post-surgery care, ensuring the dog heals quickly and comfortably. Getting Your Dog Neutered, By choosing to neuter a dog, owners are not only taking a step toward responsible pet ownership, but they are also actively contributing to community animal welfare by helping reduce the number of homeless dogs.
In conclusion, dog neutering through male dog castration is a safe, widely practiced, and highly beneficial procedure. With proper veterinary supervision, the neuter procedure provides long-term health advantages, behavioral improvements, and supports the overall well-being of both pets and their owners.

Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System in Dogs
Understanding male dog anatomy is essential for every pet owner who wants to ensure their dog’s health and reproductive well-being. A male dog has two dog testicles, which are housed in the scrotum location between the back legs. Getting Your Dog Neutered, These testicles play a crucial role in sperm production and the secretion of testosterone in dogs, a key male sex hormone responsible for the development of male dog characteristics and influencing sexual behavior in dogs.
Also Read: How Many Teeth Do Dogs Have
Each testicle contains an epididymis, where sperm maturation occurs. The epididymis connects to the vas deferens, a tube that carries sperm during ejaculation. The semen transport system is further supported by the prostate gland, which produces the fluid portion of semen, aiding in safe and effective reproduction. Getting Your Dog Neutered, The prostate function is essential not only for semen quality but also for the overall health of the male reproductive system.
During mating, sperm travels from the vas deferens into the urethra in dogs, which serves as the passageway for semen to exit the body. The dog penis is covered by a sheath of skin known as the prepuce, which protects it when not erect. When the dog is sexually aroused, the penis enlarges and extends from the prepuce, facilitating the dog mating process.
A healthy reproductive system in male dogs is vital for breeding purposes, but it also plays a role in maintaining hormone balance, behavior, and overall physical health. Getting Your Dog Neutered, Regular veterinary check-ups can help monitor canine reproduction and detect any issues early, such as infections, prostate problems, or abnormalities in sperm production.
By understanding these key aspects of male dog anatomy, including dog testicles, epididymis function, vas deferens, and prostate gland, owners can make informed decisions about care, neutering, or breeding. Awareness of testosterone in dogs and its influence on sexual behavior in dogs helps in managing behaviors like marking, roaming, or aggression, ensuring a happier relationship between pets and owners.
In summary, the male dog’s reproductive system, from sperm production to semen transport, plays a crucial role in canine reproduction. Getting Your Dog Neutered, Knowledge of this system empowers owners to provide better care and maintain their dog’s health, behavior, and overall well-being.
Also Read: Where to Buy a German Shepherd Puppy
Why Would a Dog Need To Be Neutered
Dog neutering benefits extend far beyond simply preventing unwanted puppies. One of the primary reasons for neutering a male dog is the prevention of reproduction. A neutered dog cannot breed, meaning he will not be able to get a female dog pregnant. Getting Your Dog Neutered, This is a crucial step in dog breeding prevention and helps control the overall pet population, which is a responsibility every pet owner should take seriously.
Another important aspect of neutering is the reduction of unwanted male behaviors. Intact male dogs are often prone to urine marking in dogs, increased dog aggression, and escaping to find mates. Neutering reduces testosterone production in dogs, which in turn diminishes these behaviors. Getting Your Dog Neutered, A calmer, less aggressive dog is easier to manage and creates a safer home environment. These improvements in behavior highlight the male dog behavior management benefits of neutering and reinforce the role of responsible dog ownership.
Occasionally, a male dog may be affected by a condition known as cryptorchid dogs, where one or both undescended testicles fail to descend into the scrotum. Although these testicles usually do not produce working sperm, they continue to produce testosterone. Getting Your Dog Neutered, As a result, the dog may still exhibit intact male traits such as marking or attempting to escape to find mates. Moreover, cancer risk in cryptorchid dogs is significantly higher, making it essential to perform neutering cryptorchid dogs for their health and safety.
Beyond behavioral improvements and reproductive control, neutering also contributes to overall dog reproductive health and canine health care. Getting Your Dog Neutered, By reducing hormone-driven behaviors and preventing reproductive organ-related diseases, neutering helps ensure a longer, healthier life for your dog. Additionally, neutering supports pet behavior control, making it easier to integrate your dog into family life and social situations without the stress of unwanted behaviors.
In summary, the neutering importance cannot be overstated. It not only prevents reproduction and reduces problematic behaviors but also protects dogs from certain health risks, especially in cases of cryptorchidism. Neutering is a vital part of responsible dog ownership, promoting the well-being of both the dog and the broader community while supporting effective canine health care and male dog behavior management.
Benefits of Dog Neutering
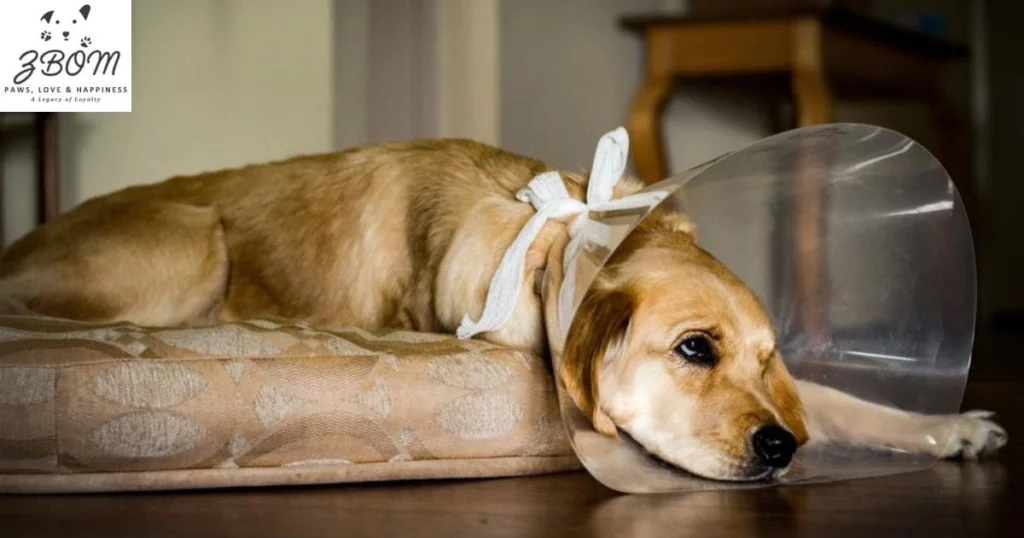

Benefits of dog neutering include:
- Removes risk of accidental pregnancy of female dogs in home
- Helps with pet overpopulation
- Reduces unwanted male behaviors, such as escaping to find mates and urine marking
- Reduces risk of traumatic injury and contracting infectious disease while roaming
- Leads to a longer average lifespan due to fewer injuries and infections
- Removes risk for testicular cancer
Effectiveness of Dog Neutering
Dog neutering effectiveness is well-documented and provides multiple benefits for both dogs and their owners. Getting Your Dog Neutered, A successful neuter procedure ensures that a male dog is unable to breed, effectively preventing reproduction and helping control the pet population. This is one of the most significant aspects of responsible dog ownership, as it prevents unwanted puppies and contributes to community animal welfare.
One of the most notable benefits of neutering is reducing unwanted male behaviors. Dogs that are neutered early often show fewer tendencies toward urine marking in dogs, dog aggression, and other problematic behaviors. Getting Your Dog Neutered, Early neutering benefits are especially important because if neutering occurs before these behaviors develop, the likelihood of them appearing is greatly reduced. Conversely, dogs whose reinforced male behaviors have already become habits may not completely stop after being neutered, although improvements are still possible.
Neutering also reduces the drive for seeking mates in dogs, which directly contributes to roaming behavior reduction. This lowered urge to roam not only makes managing your dog easier but also improves pet safety. Getting Your Dog Neutered, Dogs that roam less are less likely to encounter hazards such as traffic, aggressive animals, or environments where they could contract an infectious disease, thus lowering their vehicle accident risk and improving overall well-being.
Health benefits are another critical advantage of neutering. Studies show that neutered males tend to have a longer neutered dog lifespan compared to intact male dogs. This is linked to reduced risks of certain cancers, fewer injuries, and decreased stress-related behaviors. Through behavior management in dogs and male dog behavior control, neutering creates a safer, calmer, and more predictable companion.
Getting Your Dog Neutered, In addition to behavioral and health improvements, neutering supports canine health improvement over the long term. It minimizes hormone-driven issues while promoting overall well-being, making it a vital component of neutering advantages for any responsible pet owner.
In summary, a successful neuter procedure is a practical and humane way to prevent reproduction, control undesirable behaviors, enhance pet safety, and improve the overall health and longevity of your dog. Understanding the full range of neutering advantages helps owners make informed decisions, ensuring their pets lead happier, healthier lives.
Cost of Dog Neutering
A routine dog neutering at a private practice is likely to cost $300 to $500.
Some low-cost or non-profit clinics have a much lower dog neutering cost. Occasionally, these clinics may hold free neuter events.
The cost will be higher if the dog is cryptorchid, especially if the veterinarian must search in the abdomen for the testicle or testicles.
Preparation for Dog Neutering
Proper dog neutering preparation is essential to ensure a safe and smooth surgical experience for your pet. Getting Your Dog Neutered, One of the first steps involves fasting before surgery. Pet parents are usually advised to withhold food from their dog the night before the procedure to reduce the risk of vomiting while under anesthesia for dogs. In many cases, water intake before neutering is still allowed, but it’s important to follow veterinarian guidance to avoid complications.
A responsible pet owner should also consider surgical recovery planning in advance. Preparing a quiet, comfortable space at home and having supplies like soft bedding, a cone collar, and medications ready will make the dog neutering procedure less stressful for the pet. Understanding the recovery process is a key part of pet parent guidance and ensures the dog heals safely.
At the veterinary hospital, the dog is anesthetized using gas anesthetics for dogs, often delivered through a trachea tube in dogs or a face mask. This ensures the pet receives oxygen during surgery and remains completely pain-free throughout the procedure. For added safety, some dogs may receive a catheter placement in dogs to allow fluid and medication administration during surgery, maintaining proper hydration and supporting recovery.
Before making the incision, the scrotum shaving and cleaning of the area in front of the scrotum is performed to ensure a clean surgical incision, reducing the risk of infection. Veterinarians emphasize surgical safety for pets at every stage, from preparation to recovery, and encourage pre-surgery care to minimize stress for both the dog and the pet parent.
Supporting your dog through this process is part of responsible pet care. Understanding each step of the veterinary surgery preparation, from fasting and water guidelines to anesthesia and post-operative care, ensures a smooth experience. With proper dog surgery support, most dogs recover quickly and experience minimal discomfort, returning to their normal, happy lives within days.
In summary, careful dog neutering preparation combined with attentive pre-surgery care and proper surgical recovery planning helps make the dog neutering procedure safe and successful. Following veterinarian guidance and providing the right support demonstrates true responsible pet care and ensures your dog’s health and well-being.
Complications of Dog Neutering
While dog neutering is a common and generally safe procedure, it is important for pet owners to understand potential dog neuter complications. Like any surgery, there are risks involved, and being aware of them helps in canine health monitoring and proper post-operative care. One of the most frequent issues is incision infection in dogs, which can occur if the surgical site is not kept clean. Minor post-surgery bleeding and scrotal swelling in dogs, sometimes resulting in a scrotal hematoma, may also occur but usually resolve with proper care and veterinary guidance.
Since dog neutering is an anesthetic procedure, there are anesthesia risks in dogs. Although rare, anesthetic complications can include inhaling vomit under anesthesia, allergic reaction to anesthetics, or, in extremely uncommon cases, cardiac arrest in dogs. The overall neuter procedure mortality rate is very low; studies show that it is a low-risk dog surgery, with only around 1 in 11,000 dogs experiencing death related to the procedure.
Beyond immediate surgical risks, research continues into the neutering long-term risks. Scientists are investigating whether neutering affects the development of orthopedic conditions in dogs, such as cranial cruciate ligament rupture, commonly known as a torn ACL in dogs, and hip dysplasia in dogs. Additionally, potential cancer risks in neutered dogs are being studied, including prostate cancer in dogs, transitional cell carcinoma, osteosarcoma, and hemangiosarcoma.
Another long-term consideration is obesity in neutered dogs, as hormonal changes can influence metabolism and appetite. Proper pet weight management is essential to minimize health problems and maintain overall well-being.
While some correlations have been observed between neutering and these risks, causation has not been definitively proven. Ongoing dog neutering research continues to shed light on these connections, helping veterinarians and pet owners make informed decisions.
In conclusion, while dog neuter complications and long-term risks exist, understanding them and following professional guidance ensures the procedure remains a safe, responsible choice. With careful canine health monitoring, proper care after surgery, and attention to pet weight management, neutered dogs can lead healthy, happy lives while benefiting from the behavioral and reproductive advantages of neutering.
Alternatives to Dog Neutering
While dog neutering is the most common method for controlling reproduction in male dogs, some pet owners may seek alternatives to dog neutering. These options are limited and less widely offered by veterinary clinic options, but they do exist for owners who want to manage their dog’s fertility while maintaining certain behaviors.
One alternative is a dog vasectomy, which renders a dog canine infertility. During this procedure, the vas deferens are cut or blocked, preventing sperm from reaching the urethra. However, a vasectomized dog will continue to produce testosterone, meaning testosterone-driven behaviors in dogs will persist. The dog may still display mating behavior in dogs and show interest in female dogs, but he will be unable to impregnate them. This method allows owners to maintain reproductive control without fully altering hormone levels.
Another less common option is chemical sterilization in dogs, typically involving a calcium chloride injection directly into the testicles. This method is considered a rare dog sterilization procedure and is categorized under non-surgical dog sterilization. Like a vasectomy, it achieves canine infertility while allowing continued male hormone production, meaning the dog may still exhibit some intact behaviors. These canine sterilant methods are used in limited situations and require careful administration by a veterinarian.
Both approaches focus on dog fertility management and reproductive control in dogs while offering alternatives to full neutering. They may appeal to owners who wish to maintain certain behaviors in their pets, but they do not eliminate all risks associated with intact male dogs. Consequently, behavior management in intact dogs remains necessary.
Choosing neutering alternatives requires thoughtful consideration and professional advice. Pet owners must weigh the benefits of retaining natural hormone levels against the continued risk of testosterone-driven behaviors in dogs. Proper planning ensures effective dog breeding prevention while supporting pet reproductive health.
Ultimately, exploring these options reflects responsible pet ownership. With veterinary guidance for sterilization, owners can make informed decisions that suit their dog’s lifestyle, health, and behavior, balancing fertility control with the desire to preserve natural hormonal influences. While not as common as traditional neutering, these methods offer flexibility for specific needs and demonstrate the range of care available in modern veterinary practice.
Conclusion
Getting your dog neutered is one of the most responsible choices a pet owner can make, offering benefits that extend beyond simply preventing unwanted litters. The procedure ensures your dog cannot reproduce, which helps control the pet population and reduces the number of dogs entering shelters. By addressing the reproductive capabilities of your dog, you are taking a proactive step toward responsible pet ownership and promoting the overall well-being of both your pet and the community.
Beyond reproduction, neutering has a profound effect on your dog’s behavior and health. Intact male dogs often exhibit behaviors driven by testosterone, such as roaming, aggression, and urine marking. Neutering reduces these tendencies, making dogs calmer, more manageable, and safer around other pets and people.
While early neutering is most effective in preventing the development of these unwanted behaviors, even dogs neutered later in life often experience improvements. Additionally, neutering decreases the risk of certain reproductive cancers and other health issues, contributing to a longer, healthier life for your pet.
It is important to remember that neutering is a surgical procedure, and like any surgery, it carries minimal risks. However, with proper veterinary guidance, careful preparation, and attentive post-operative care, most dogs recover quickly and without complications. Pet parents should also monitor their dog’s weight and overall health after the procedure to prevent obesity and ensure continued wellness.
In conclusion, neutering your dog is a safe, common, and beneficial procedure that enhances quality of life, improves behavior, and supports long-term health. By choosing to neuter, you are taking a responsible, informed step as a pet owner, ensuring your dog lives a happier, healthier, and more balanced life. With thoughtful planning, proper care, and veterinary support, neutering becomes not just a medical procedure, but a meaningful investment in your dog’s well-being and your peace of mind.
FAQ
Is it a good idea to get my dog neutered?
Neutering boosts reproductive health in dogs, reduces pregnancy-related risks, life-threatening infections, and cancer, ensuring pet wellness with veterinary guidance.
What is the ideal age to get a dog neutered?
Most dogs can have 6 months neutering, but veterinary guidance for neutering considers breed, size, and development to ensure responsible pet care and dog health planning.
Does a dog change after being neutered?
Neutering leads to behavioral changes after neutering, reducing roaming and escaping, improving dog behavior and safety, thanks to lowered testosterone effects in dogs.
Is it painful for dogs to get neutered?
A dog neuter procedure or male dog castration removes testicles under general anesthesia, ensuring a pain-free dog surgery and safe, responsible canine surgical procedure.
Are dogs happier after being neutered?
Neutering reduces male dog aggression over time, improving neutered dog temperament, creating calmer male dogs, and supporting pet behavior improvement and happiness.







